Subnets are the logical network that you group your resources in a single local network. Communication in and out of a subnet is of critical importance, and a routing table contains the rules on how traffic can be directed.
Subnets
After creating a VPC, you can add one or more subnets in each AZ. Each subnet resides entirely within one AZ and cannot span AZs.
- A subnet is an isolated local network confined in a single AZ.
- Different application tiers are in different subnets.
- 5 IPs are reserved for a subnet (ex. /24 network – 251 IPs available)
- 0 (first) – Network
- 1 – Router
- 2 – DNS
- 3 – for future use
- X (last) – Broadcast
- Subnets must be associated with a route table.
- The CIDR block of a subnet cannot overlap the CIDR blocks of other subnets in the same VPC.
- Public or Private
- Subnets are by default private unless created in a default VPC.
- A public subnet has a route to the internet.
- It is associated with a route table that has an IGW attached.
Route Tables
A route table contains a set of rules (routes) that are used to determine where traffic is directed.
- Only one route table can attached to a subnet, but, unlike an IGW, you can have multiple active route tables in a VPC.
- Each VPC has a virtual routing device called the VPC router.
- You cannot delete a route table if it is associated with subnets.
Route Rules
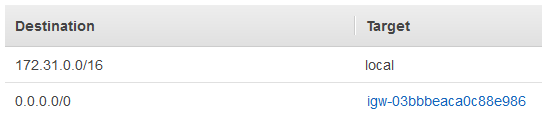
- A Route Table has a collection of rules, called routes. A route contains a destination and a target.
- Destination
- the target CIDR block range of traffic
- Target: where traffic is routed
- local: inside the VPC
- instance
- Internet Gateway
- Other connections such as NAT Gateway, Transit Gateway, Virtual Private Gateway, …
- Destination
- By default, all subnets’ traffic is allowed within a VPC, which is called a local route.
- If multiple routes apply, the most specific one is chosen (/32 is chosen before /24).
- A default route (0.0.0.0/0 or ::/0) can be added to match any traffic, which are not already matched.
- The default VPC already has a main route table: local route + IGW
Public Subnets
- Subnets can be public or private.
- A subnet is public when:
- The subnet has a public IP or EIP; You can modify auto-assigned IP settings for a subnet.
- VPC has an Internet Gateway.
- The subnet has a route to send all non-local traffic to the Internet Gateway.
- Network ACL and security groups allow sending and receiving traffic from the Internet.
Notes
- CIDR Visualizer: https://cidr.xyz
- Subnet Calculator (IPv4): https://www.site24x7.com/tools/ipv4-subnetcalculator.html