Here is the confusing part. AWS provides multiple auto scaling services: notably ASW Auto Scaling and EC2 Auto Scaling.
- AWS Auto Scaling lets you configure and manage scaling for your scalable AWS resources through a scaling plan.
- EC2 Auto Scaling is an AWS service that automatically increases or decreases the number of on-demand instances based on chosen CloudWatch metrics.
In short, AWS Auto Scaling is an extension to EC2 Auto Scaling and scales a collection of related resources. You need to create a scaling plan, which is a collection of scaling instructions for multiple AWS resources.
- You can use EC2 Auto Scaling when you scale only EC2 instances.
AWS Auto Scaling
- You should use AWS Auto Scaling to manage scaling for multiple resources across multiple services.
- You can include existing EC2 Auto Scaling groups to an AWS auto scaling plan.
- To scale resources other than EC2, use the Application Auto Scaling API, which allows you to define scaling policies to scale your AWS resources automatically.
- Uses Cases of AWS Auto Scaling
- Auto scaling EC2 instances in an auto scale group
- Spot Fleet requests
- ECS services
- Aurora read replicas
- DynamoDB tables and global secondary indexes
EC2 Auto Scaling
Auto Scaling Components
- You need to create an auto scaling group to specify what to scale, such as web servers or application servers.
- An auto scaling group uses the scaling options to determine how to scale based on the specified conditions (a dynamic scale) or on the schedule.
- An auto scaling group uses a launch template (or configuration) to launch a new EC2 instance.
Launch Templates
- A Launch Template is an instruction on how to create a new instance.
- AMI, Instance type, Storage, Key pair, IAM role, User data, Purchase option, Security groups
- It includes Tagging and more advance instance/purchasing options.
- Launch Templates cannot be edited after creation.
- A new configuration should be created with a new version.
- Advanced Settings
- Termination Protection:
- Once it is enabled, an instance cannot be terminated using Console, API, or CLI until the setting is disabled.
- Instance Auto-recovery
- Termination Protection:
Auto Scaling Groups
Auto Scaling Group is a logical grouping of EC2 instances for scaling and management.
You can configure the AGS (Auto Scaling Group) like this:
- Launch Template
- Pick your Launch Template
- Select the version
- Networking and Purchasing options
- Select the VPC and Subnets
- can be configured to use multi-AZs to improve high availability.
- Instance Purchase Options
- Instance distribution (% On-demand & % Spot) – Spot Fleet
- Override the instance type requirements (from the launch template)
- vCPUs, Memory, …
- Select the VPC and Subnets
- Load Balancing and Health Check
- Attach the load balancer if needed
- VPC Lattice Integration Options
- VPC Lattice facilitates communications between AWS services and helps you connect and manage your applications across compute services in AWS.
- Select the Health Check Type
- EC2 health check is always enabled
- Optionally, you can enable ELB health check, or VPC Lattice health check.
- Health Check Grace period: delays the first health check until the instance finishes initialization. (300 seconds by default)
- When the health check fails, ASG terminates the instance and launch a new instance.
- Note that ASG does not keep the unhealthy instance.
- Monitoring
- Enable “group metrics collection” within CloudWatch
- You can enable “default instance warmup” time.
- The amount of time that CloudWatch metrics for new instances do not contribute to the group’s aggregated instance metrics, as their usage data is not reliable yet.
- Auto Scaling Group Size
- Set the initial size of ASG – Desired Capcity
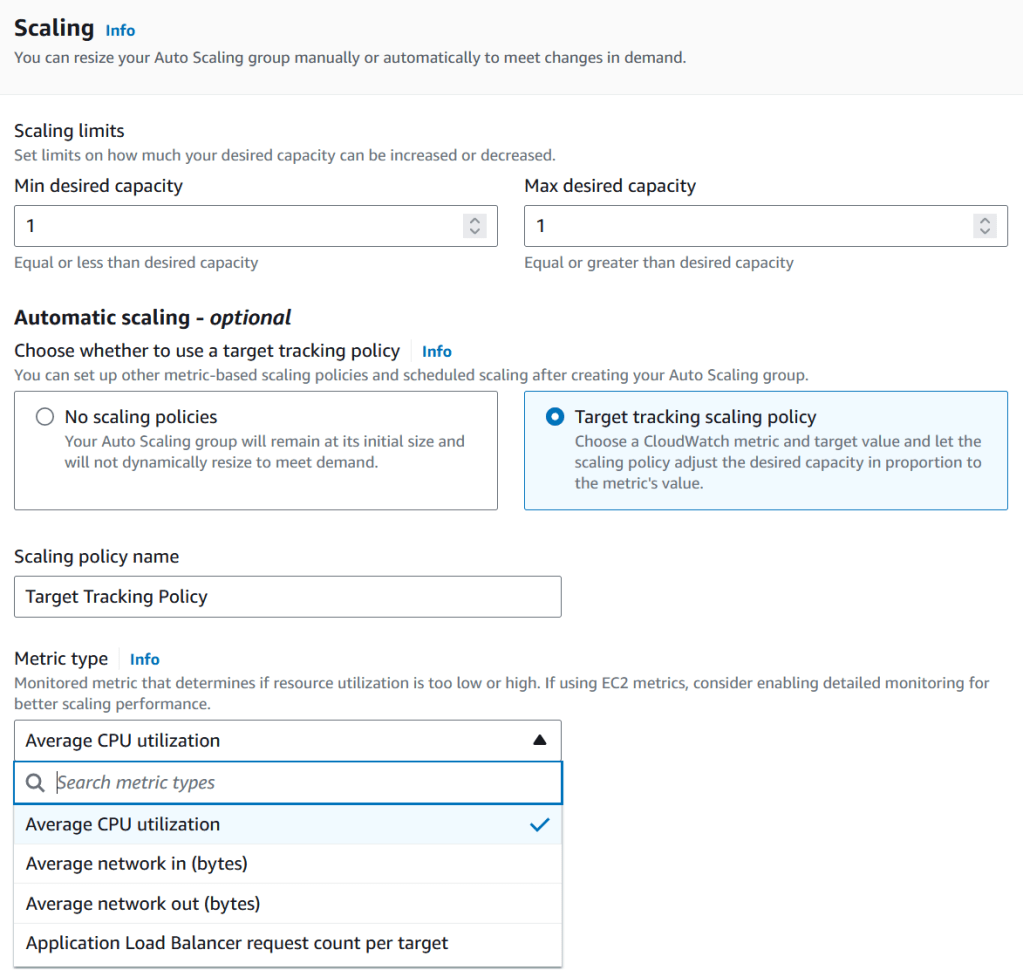
- Scaling Options
- Scaling Limits
- Min Capacity
- Max Capacity
- Automatic Scaling
- No scaling policies (Manual)
- The ASG remains at the initial size.
- Target tracking scaling policy
- based on the metrics (such as CPU Usage, Network In/Out, ALB Request Count)
- No scaling policies (Manual)
- Scaling Limits
- Notification
- Send notifications to SNS topics
Metrics
The following metrics can be used to scale resources:
- CPUUtilization
- RequestCountPerTarget
- Average Network In/Out
EC2 Auto Scaling Options
Once you created the ASG, you can fine-tune the scaling policies.
Manual Scaling
- It is the most basic option, and you update the options manually
- minimum
- The lowest number of EC2 instances that are running
- At least 2 for high availability
- maximum
- The highest number of EC2 instances that are running
- You will never have more instances than this number.
- desired
- The number of instances you want right now.
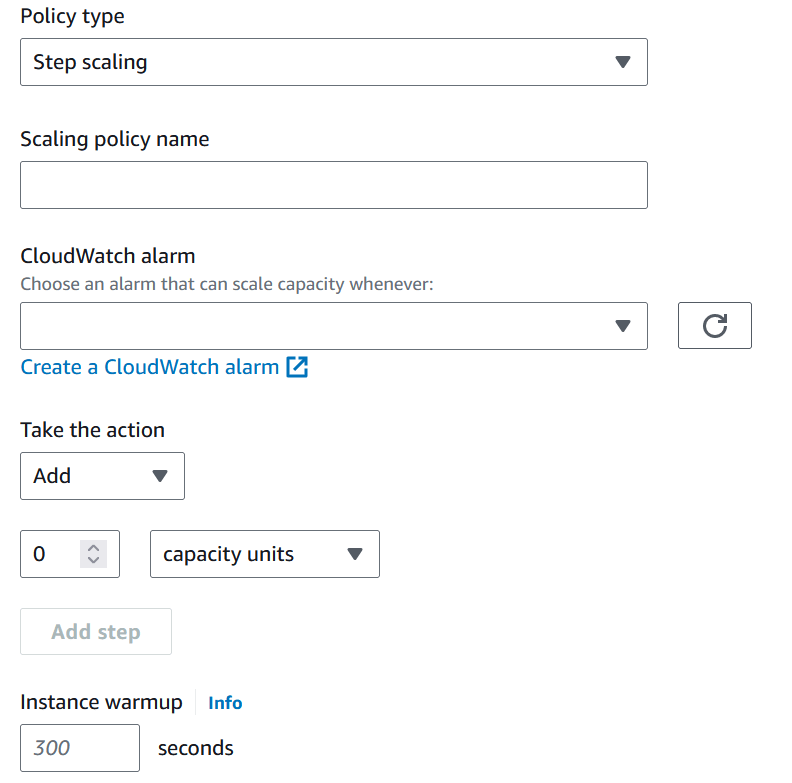
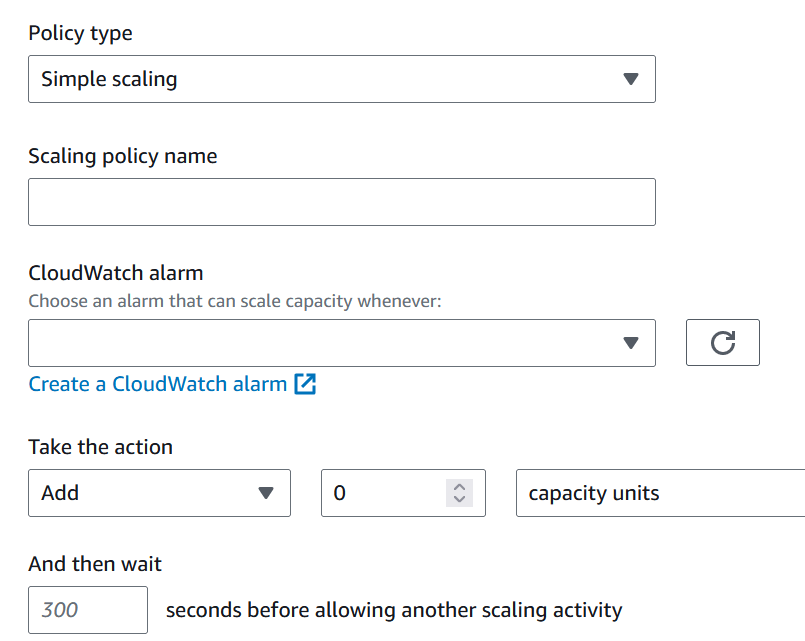
Automatic Scaling – Dynamic Scaling Policy
| Target tracking scaling | Step scaling | Simple scaling | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | the target value for a specific metric | a set of scaling adjustments, known as step adjustments | a single scale adjustment |
| Triggers | Metric type & Target Value | Cloud Watch Alarms | Cloud Watch Alarm |
| Actions | Steps as a set of actions: Add, Remove, or Set to | A single action: Add, Remove, or Set to | |
| Example | Keep the average CUP utilization at 70% | When a CloudWatch alarm (CPU < 30%) triggers, set to 1 instance When a CloudWatch alarm (CPU > 30%) triggers, add 1 instance When a CloudWatch alarm (CPU > 70%) triggers, add 2 instances | When a CloudWatch alarm (CPU > 70%) triggers, add 1 instance |
| Cooldown Period | NOT applied | NOT applied | Applied |
[Note] The cooldown period (300 seconds default) is a setting that ensures not to launch or terminate additional instances during the cooldown period when the scaling action happens. It applies to Simple scaling but not for target tracking, step, or scheduled scaling.

Automatic Scaling – Predictive Scaling Policy
- It looks at historic traffic patterns and forecasts them into the future to schedule changes.
Scheduled Scaling
- The scaling is done automatically based on specified time and date.
- You create a scheduled action, which performs a scaling action at specified times. To create a scheduled scaling action, you specify the start time when the scaling action should take effect, and the new minimum, maximum, and desired sizes for the scaling action.
- Recurrence
- Once, Cron, or Every (5 mins, 30 mins, …)
- It is useful when the workload is predictable.
Auto Scaling Health Checks
- Health Checks identify any instances that are not healthy
- EC2 status checks (default)
- ELB health checks
- Custom health checks
- Unhealthy instances are terminated and new instances are created based on the health checks.
- Auto Scaling can send SNS notifications when scaling occurs.
Achieving Highly Available and Fault-tolerant Architecture
- Deploy instances in different AZs
- To achieve fault-tolerance, you need to provision redundant resources, which entails an extra cost.
EC2 Auto Scaling lifecycle hooks
Lifecycle hooks are used to perform custom actions by pausing instances when an Auto Scaling Group launches or terminates them.
- Lifecycle
- autoscaling:EC2_Instance_Launching: before an instance is in service
- Pending
- Pending:Wait
- Pending:Proceed
- InService
- autoscaling:EC2_Instance_Terminating: before an instance is terminated
- Terminating
- Terminating:Wait
- Terminating:Proceed
- Terminated
- autoscaling:EC2_Instance_Launching: before an instance is in service
- When an instance is paused, it remains in a wait state until the lifecycle action is completed.
- By default, an action is completed when the timeout period ends. But you can complete the action with complete-lifecycle-action command.
- Lifecycle hooks can be used to install or configure software on instances before they start receiving traffic or do some cleanup actions before instances are terminated.
- You can use EventBridge rules to receive the event.
{
"version": "0",
"id": "468fe059-f4b7-445f-bb22-2a271b94974d",
"detail-type": "EC2 Instance-terminate Lifecycle Action",
"source": "aws.autoscaling",
"account": "123456789012",
"time": "2015-12-22T18:43:48Z",
"region": "us-east-1",
"resources": ["arn:aws:autoscaling:<region>:<account>:autoScalingGroup:..."],
"detail": {
"LifecycleActionToken": "630aa23f-48eb-45e7-aba6-799ea6093a0f",
"AutoScalingGroupName": "sampleASG",
"LifecycleHookName": "SampleLifecycleHook-6789",
"EC2InstanceId": "i-12345678",
"LifecycleTransition": "autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATING"
}
}
EC2 Auto Scaling SNS Notification
ASG can send a notification via SNS for the following events:
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH_ERROR
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE_ERROR
EC2 Auto Scaling Termination Policies
You can determine which instance is terminated first when the ASG scales down or the instances are refreshed. You can combine policies with the evaluation order.
- Default Termination
- Select an AZ with the largest number of instances
- Terminate the instance with the oldest Launch Template
- If the instances are still in the same launch table, terminate the instance that is closest to the next billing hour
- AllocationStrategy
- e.x) lowest price for Spot Instances
- OldestLaunchTemplate
- CloestToNextInstanceHour
- NewestInstance
- OldestInstance
- Custom – backed by a Lambda function
EC2 Auto Scale Warm Pools
You can reduce the latency of launching new instances using ASG warm pools.
- Instances are pre-initialized.
- After creating instances in the warm pool, you can move the instance to the stopped or hibernated state for cost saving.
- Settings
- Minimum Warm Pool size
- Max Prepared Capacity (MAX capacity of ASG by default)
- Warm Pool instance State
- Running
- Stopped
- Hibernated
| Running | Stopped | Hibernated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale out | Fastest – immediate | Slow – need to be started | Medium – need to be waked, applications are already in memory |
| Cost | High – paying all the time | Low – paying the attached volume only | Low – paying the attached volume only (might need a bigger volume) |
- Instance Reuse Policy
- When the scale-in event occurs, the active instance might be moved back to the warm pool.
- Warm pool Lifecycle Hooks
- Warmed:Pending
- Warmed:Pending:Wait
- Warmed:Pending:Proceed
- Warmed:Running, Warmed:Stopped, Warmed:Hibernated
Task – Recreate all EC2 Instances with a new AMI
- Create a new Launch Template with a new AMI
- Set the minimum healthy percentage (such as 60%)
- Call the API StartInstanceRefresh
- Old instances are destroyed and new instances are created.