Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage service that allows you to migrate data into AWS, extending on-premise storage capacity using AWS.
Features
- It is used when you want to integrate the existing on-premise application data with AWS cloud storage services without fully migrating to AWS.
- Applications in your network can access data in the cloud.
- Data may be moved to AWS and cached them locally at the on-premise data center.
- Key Management Service (KMS) can encrypt data at rest in the cloud.
- CloudWatch can be used for monitoring, and CloudTrail can be used for logging account activity.
Use Cases
- Reduce on-premises storage with cloud-backed file shares
- Provide on-premises applications low latency access to data stored in AWS
File Gateway
File Gateway is a file-based interface to S3.
- It stores data in S3 and offers SMB (Server Message Block) or NFS (Network File System)-based access to the data.
- A software appliance or a Gateway is deployed in EC2 instances or on-premise environment (VMs).
- Recently accessed data is cached in the gateway.
- Stalled Objects
- If you push the file directly to S3, you might not see the files through the file gateway.
- Manually, you can call “RefreshCache” api to synch the gateway.
- Or you can run the Lambda function on schedule (via EventBridge) to execute “RefreshCache“.
- Once in S3, you can access the objects directly or manage them using features such as S3 lifecycle policies and cross-region replication.
- File Gateway supports S3 Standard, IA, or One-zone IA. You cannot transfer files directly to Glacier, but you can set the lifecycle policy. If an application attempts to access a file in Amazon S3 Glacier, you will receive a generic I/O error.
- File Gateway integrates with Microsoft Active Directory on-premises as well as with in-cloud Active Directory solutions such as Managed Microsoft AD.
How does the File Gateway Work?
- Specify how much disk space you want to allocate for local cache.
- The local cache acts as a buffer for writes and provides low latency access to data that was recently written to or read from Amazon S3.
- When a client writes data to a file via File Gateway, that data is first written to the local cache disk on the gateway itself.
- File Gateway transfers the data to the S3 bucket asynchronously in the background, optimizing data transfer using multipart parallel uploads and encrypting data in transit using HTTPS.
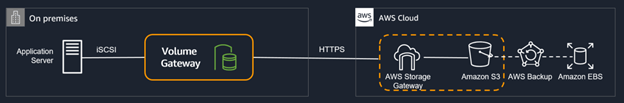
Volume Gateway
- Applications access data in the volume storage in AWS using iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) connectivity.
- Data on the volumes are stored in Amazon S3, and you can take point in time copies of volumes, which are stored as Amazon EBS snapshots. You need to mount the entire volume to access data.
- Volumes are stored in an Amazon S3 bucket maintained by the AWS Storage Gateway service. Your volumes are accessible for I/O operations through AWS Storage Gateway. You cannot directly access them using Amazon S3 API actions.
- Types
- Stored Volumes: Data are stored at the on-premise data center and backed up to AWS using snapshots.
- Cached Volumes: Data are stored in S3 and cached in the on-premise data center for fast access.
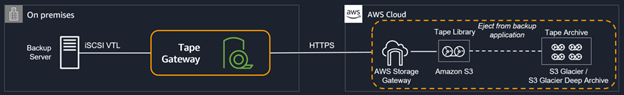
Virtual Tape Gateway (VTL)
- Cost-effective, long-term data archiving.
- Virtual tapes are available for immediate access and are backed by Amazon S3.
- Tapes can be archived. Archived tapes are stored in Amazon S3 Glacier or Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive.