Stacks take logical resources from a template and create, update, or delete physical resources in AWS. In this post, we can delve into advanced feature of stacks.
StackSets
A StackSet lets you create, update, and delete CloudFormations stacks across multiple AWS accounts and regions in a single operation.
- Manage accounts in AWS Organizations
- It will reduce management overhead.
- You can automatically deploy StackSets to a new account added to AWS Organization
- Troubleshooting
- A Stack operation fails and the status is “OUTDATED”
- The target account does not have proper permissions to create the resources.
- The admin account does not have a trust relationship with a target account.
- You reached the limit or the quota in the target account.
- A Stack operation fails and the status is “OUTDATED”
StackSets – Service Managed Permissions
- With service-managed permissions, you can deploy stack instances to accounts managed by AWS Organizations in specific Regions.
- With this model, you don’t need to create the necessary IAM roles.
- StackSets create IAM roles enabling trusted access within AWS Organizations on your behalf.
- Must enable all features (not just billing) in AWS Organizations
StackSets – Self Managed Permissions
- With self-managed permissions, you can deploy stack instances to specific AWS accounts in specific Regions.
- To do this, you must first create the necessary IAM roles to establish a trusted relationship between the account you’re administering the stack set from and the account you’re deploying stack instances to.
- Grant self-managed permissions – AWS CloudFormation (amazon.com)
In your administrator account:
- Create a role (Admin account)
- AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole
- allows the admin account to assume the stack set execution role
- AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole"
],
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}
- Setup the Trust Relationship (Admin account)
- The CloudFormation service is trusted to assume the stack set admin role
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "cloudformation.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
In each of your target accounts:
- Create a role
- AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole
- defines the permissions that need in the target account
- AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action":
[
"cloudformation:*",
"s3:*",
"sns:*",
"ec2:*"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
- Setup the Trust Relationship (Target account)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::{admin_account_id}:root"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Protecting Stacks
Termination Protection
- You can activate “Termination Protection“.
- Delete Stack actions will be denied.
- For nested stacks, the protection cascades to child stacks.

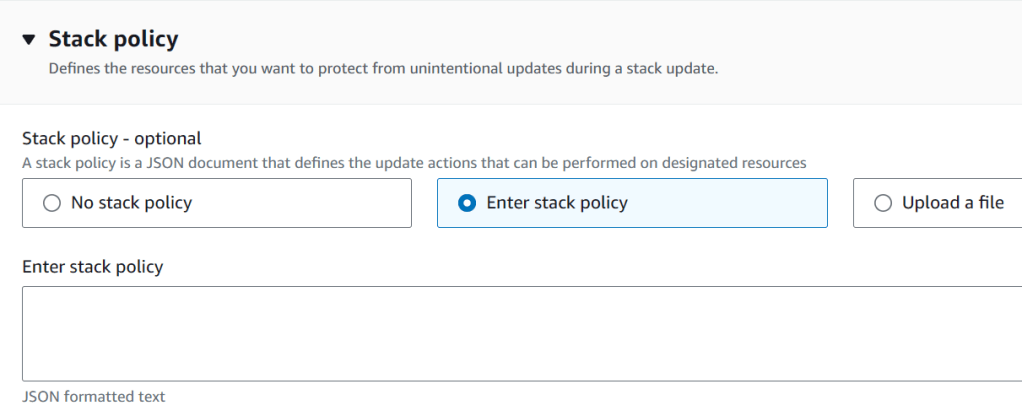
Stack Policy
- You can prevent resources from being unintentionally updated or deleted during a stack-update by using a stack policy.
- A stack policy is a JSON document that defines which actions can be performed on designated resources.
# allow updates on all resources except the production database
{
"Statement" : [
{
"Effect" : "Allow",
"Action" : "Update:*",
"Principal": "*",
"Resource" : "*"
},
{
"Effect" : "Deny",
"Action" : "Update:*",
"Principal": "*",
"Resource" : "LogicalResourceId/ProductionDatabase"
}
]
}
Deletion Policy
You can control how to do the resources when the template is deleted in the resource-level options. You can set the “DeletionPolicy” to any resource to control.
- Delete (default)
- Deletes the resource, default for almost all resources
- AWS::RDS:DBCluster -> default is Snapshot
- Special cases
- For an S3 bucket, the bucket should be empty.
- Security groups cannot be deleted until all associated EC2 instances are terminated.
- Deletes the resource, default for almost all resources
- Retain
- Keeps the resources after stack deletion
- Snapshot
- Deletes the resource but creates a snapshot as a backup
- EBS volume, ElasticCache cluster for REDIS
- RDS Instance, RedShift cluster
- Deletes the resource but creates a snapshot as a backup
Resources:
MyEC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
...
DeletionPolicy: Retain
MyDBInstance:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
Properties:
...
DeletionPolicy: Snapshot
Service Role – IAM Policy
- A Service Role controls what CloudFormation can do.
- By default, CloudFormation uses a temporary session from your user credentials.
- You can provide the custom service role:
- to achieve the least privilege principle
- to give permission that you do not have
- A user must have “iam:PassRole” permission to assign the service role to CloudFormation.
Rollback Triggers
- You can set up CloudWatch alarms and trigger the rollback.
- Monitoring time: 0 ~ 180 minutes
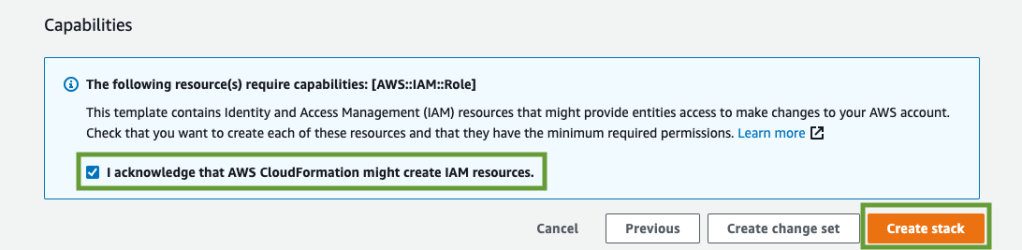
Capabilities
In some cases, you must explicitly acknowledge that your stack template contains certain capabilities in order for CloudFormation to create the stack.
- CAPABILITY_IAM & CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
- When you need to create or update IAM resources (Users, Roles, Groups, Permissions …) :
- Use “CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM” with the resources with custom names
- CAPABILITY_AUTO_EXPAND
- Some template contain macros, which perform custom processing on templates.
- If your stack template contains one or more macros, and you choose to create a stack directly from the processed template, you must acknowledge this capability.
- If you don’t specify these capabilities, CloudFormation returns an InsufficientCapabilities error.
Nested Stacks vs Cross Stacks
Nested Stacks
- You can define common components or components with repeated patterns in separate stacks and call them from other stacks.
- Examples: Security groups
- You can use the “AWS::CloudFormation::Stack” resource type to include another stack
Resources:
myStack:
Type: AWS::CloudFormation::Stack
Properties:
TemplateUrl: https://s3.amazonaws.com/mybucket/t1.template
Parameters:
... # pass parameters to another stack
Cross Stacks
- Used when stacks have different lifecycles
- How to connect stacks
- Export values in the “Outputs” section
- Import values using “ImportValue” function