CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) – lower latency, higher transfer speed, and reduced server load. It has built-in DDoS (distributed denial of service) attack protection.
Features
- CloudFront is a global service.
- The domain name is created when a distribution is created and is used to view contents in a browser.
- Objects are cached for the life of the Time to Live (TTL).
- 24 hours by default
- You can invalidate (clear) cached contents manually with some costs.
CloudFront Components
- Origin is the server or service that hosts the content.
- S3 bucket or S3 hosted website
- AWS Media Services
- Custom
- EC2 instance (must be public)
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB is public but underlying EC2 instances can be private)
- Route 53 domain
- Distribution is a CloudFront configuration of a specific implementation. It is the name that is given to the specific CDN.
- Edge Location is the location where the content is cached – local infrastructure.
- Regional Edge Cache: edge locations <- regional cache <- origin
Failover using Origin Group
An origin group includes
- Two origins
- a primary origin
- a second origin to failover
- Failover criteria
- HTTP Status Code such as 5xx
- High Availability and Failover
- Origins in a group can be across AWS Regions.
Restricting Access to ALB
When you want to secure ALB and Instances using CloudFront:
- Prevent the direct access to the ALB or Instances
- Set up the CloudFront
- Set ALB as an Origin
- In the CloudFront, add the custom HTTP header to the request to ALB
- Configure ALB to forward the requests that have the custom header to instances
Distribution and Caching
- Distribution Types:
- Web Distribution: Web Sites, HTTP/HTTPS
- RTMP Distribution: Adobe Real-Time Messaging Protocol – media streaming/flash multi-media content.
- Caching Process
- Create a distribution and point at one or more origins. A distribution has a DNS address.
- Access to the DNS address is redirected to the closest edge location.
- If the edge location has a cached copy, it is delivered (cache-hit).
- If it is not cached, the edge location attempts to download it from a regional cache or the origin (origin fetch). When an edge location receives data, it forwards data to a client and caches the data.
CloudFront Signed URLs and Signed Cookies
Both signed URLs and signed cookies control who can access content.
- A policy is attached to an URL or a cookie.
- Expiration, IP ranges, and trusted signers
- Use OAC(Origin Access Control) to restrict direct access to S3.
- Use Signed URLs for
- RTMP distributions (signed cookies do not support RTMP distributions)
- Individual files such as an installation package (1 URL is for 1 file)
- Clients who do not support cookies
- Use Signed cookies for
- Multiple files (1 cookie can be used for multiple files)
- When you do not want to change the current URLs
- You can send the required “Set-Cookie” headers only to the allowed users.
To use signed URLs or signed cookies, you need a signer.
A signer is either:
- a trusted key group that you create in CloudFront (recommended)
- works with the CloudFront API and IAM policies
- an AWS account that contains a CloudFront key pair
- Only a root account can create a key pair
Customization at the Edge
- You can customize requests and response at the CloudFront edge.
- Manipulate requests and response
- Authentication or Authorization
- Request filtering
- It is not a caching feature.
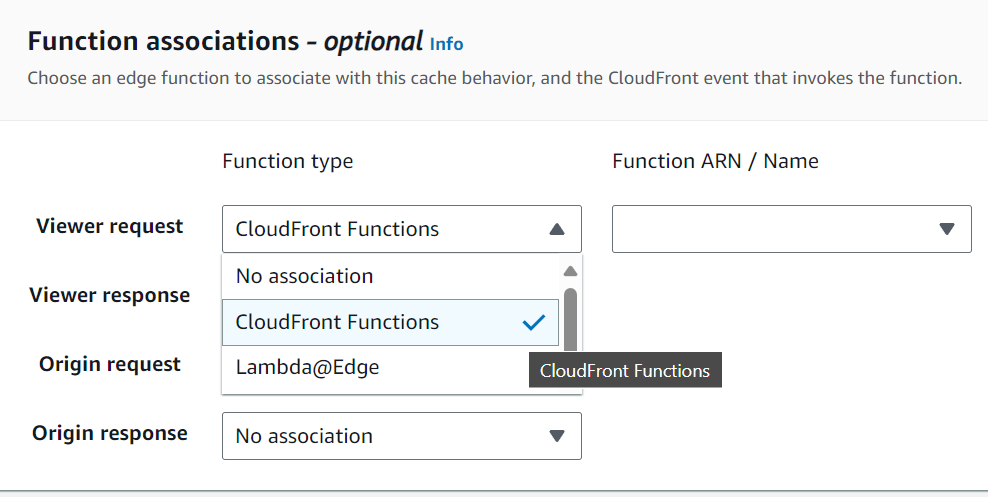
CloudFront Functions
- Lightweight functions written in JavaScript
- Native feature of CloudFront
- Run at edge locations
- Used to change viewer request and response:
- Viewer Request: after CloudFront receives a request from a viewer
- Viewer Response: before CloudFront sends the response to the viewer
Using Lambda@Edge
- By using Lambda@Edge with CloudFront, you can customize the content that CloudFront delivers, executing the functions in AWS locations closer to the viewer.
- Runs at the nearest Regional Edge Cache
- The functions run in response to CloudFront events:
- Viewer Request: after CloudFront receives a request from a viewer
- Origin Request: before CloudFront forward the request to the origin
- Origin Response: after CloudFront receives the response from the origin
- Viewer Response: before CloudFront sends the response to the viewer
- You can load different content from origins based on the request parameters such as user-agent (device type).
| CloudFront Functions | Lambda@Edge | |
|---|---|---|
| Runtime | JavaScript | Node.js, Python |
| Run at | Edge Locations | Regional Edge Locations |
| Triggers | Viewer Request Viewer Response | Viewer Request Viewer Response Origin Request Origin Response |
| Isolation | process-based | VM-based |
| Use Cases | Transform request attributes URL rewrites Request authentication | Requires a full control and more features Need to access 3rd party libraries |
| Execution Time | < 1 ms | 5 seconds (viewer triggers) 30 seconds (origin triggers) |
| Memory | < 2 MB | 128 MB (viewer triggers) 10 GB (origin triggers) |
| Network Access | No | Yes |
| File Access | No | Yes |
| Request Body Access | No | Yes |
Origin Access Control (OAC)
OAC is replacing Origin Access Identity (OAI).
- S3 as a Origin
Geo Restriction (Geo Blocking)
Geo restriction is used to prevent users in specific geographic locations from accessing content that you’re distributing through a CloudFront web distribution.
- CloudFront Geo Restriction is used to restrict access to all of the files that are associated with a distribution and to restrict access at the country level.
- Third-party geolocation service can be used to restrict access to a subset of the files that are associated with a distribution or to restrict access at a finer granularity than the country level.
- How
- Allow List: a whitelist of approved countries
- Block List: a blacklist of banned countries
CloudFront Realtime Logs
Creating realtime dashboards using Amazon CloudFront logs | Networking & Content Delivery
- Activate real-time logs on the CloudFront distribution.
- Create a stream in Amazon Kinesis Data Streams.
- Configure Amazon Kinesis Data Streams to deliver logs to Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service).
- Create a dashboard in OpenSearch Dashboards (Kibana).
CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication
- CloudFront
- via Global Edge network
- No need to set up region by region
- Content is cached for TTL
- Great for static content that must be available everywhere
- via Global Edge network
- S3 Cross Region Replication
- Must be configured for each region
- Read only
- Great for content that needs to be available in few regions