CodeCommit is a managed source – version – control service that hosts private Git repositories.
Features
- Collaboration
- Developers collaborate on code.
- Commit, branching, merging, and pull requests
- Monitoring
- Fully viewable and auditable
- High Availability and Durability
- There are no limits on file types or sizes.
- Stores your repositories in Amazon S3 and Amazon DynamoDB.
- Fully Managed
- No size-limit (Scaling)
CodeCommit Security
- Authentication
- SSH: SSH Keys in IAM
- HTTPS: AWS CLI Credential Helper or Git Credentials for IAM user
- Authorization
- IAM policies: manage permissions to repositories
- In Transit
- Encrypted using SSH or HTTPS
- At Rest:
- Encrypted using AWS KMS
- AWS Managed Key (Regional)
- Encrypted using AWS KMS
- Cross-account Access
- Use IAM roles and STS (AssumeRole API)
- Do not share SSH keys or AWS Credentials
Authentication – Accessing Repositories
You can configure your Git client to communicate with CodeCommit repositories.
- Git credentials with HTTPS Connection (Recommended)
- You can generate a static user name and password pair in the IAM console.
- Setup for HTTPS users using Git credentials – AWS CodeCommit (amazon.com)
- SSH keys with SSH
- AWS CLI credential helper with HTTP
- AWS access keys
You cannot use your IAM username and password to access CodeCommit.
Authorization Using IAM
CodeCommit is a managed AWS service and you can restrict access via IAM policies.
- Use Case 1: Grant full access except creating or deleting repositories
- Create a user group and add users
- Attach “CodeCommit Power User” policy to the group
- Use Case 2: Restrict users to push or merge code to a specific branch
- Create an IAM policy (Resource Policy is not supported) and attach it to users and groups
# Deny Push to the prod branch
"Statement": [
"Effect": "Deny",
"Action": [
"codeCommit:GitPush"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:codecommit:<region>:<account>:<repo>",
"Condition": {
"StringEqualsIfExists": {
"codeCommit:References": [
"refs/heads/prod"
]
}
}
]
Pull Requests
- Rather than pushing changes directly to the main or develop branch, you can require users to approve changes before the code is merged.
- Approval Rule Templates
- Automatically apply Approval Rules to pull requests
- You can specify different rules for different branches such as dev and prod.
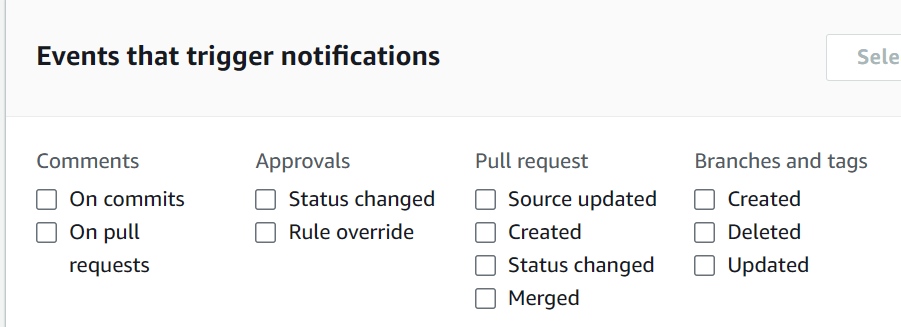
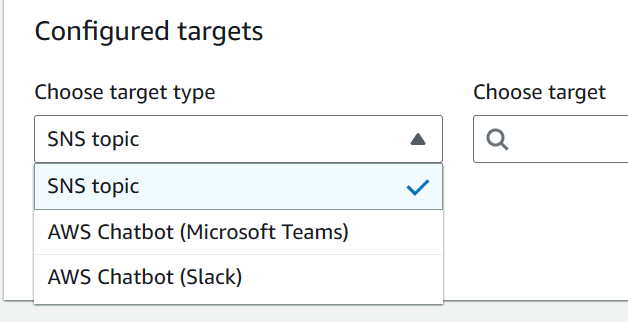
Notifications
- Notification rules set up a subscription to events that happen with your resources in the repository.
- When the events occur, notifications will be sent to the designated targets.
- SNS or Chatbot
Events Handling
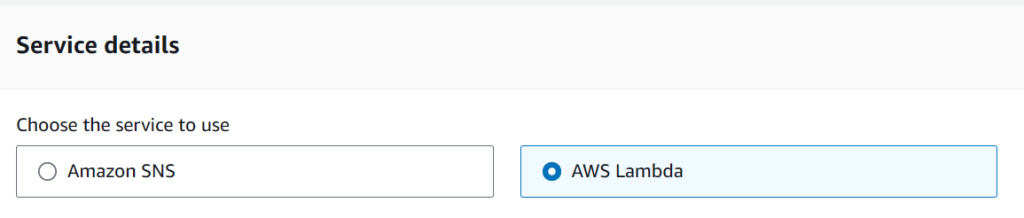
Built-in Triggers
If you need to invoke actions for some basic events, you can simply use built-in Triggers in CodeCommit.
- Events
- Push to branch
- Create a branch
- Delete a branch
- Destination
- SNS
- Lambda Function
- Up to 10 triggers per repository
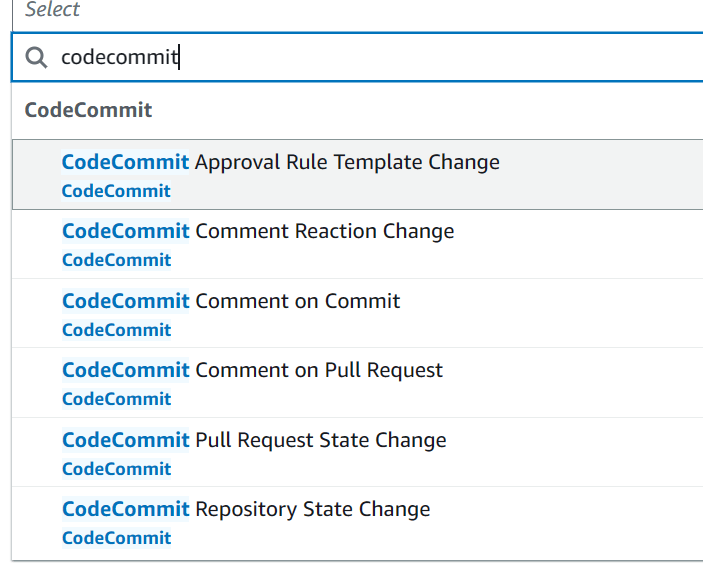
EventBridge Rules
- You can use the full features of EventBridge to handle the following events.
Cross-Region Replication
- You can replicate the code between regions. It can be done via events and actions via EventBridge.
- Lower latency pulls for global developers
- Backups
- Steps: You need to setup the CodeCommit trigger.
- CodeCommit event is triggered (Region A)
- EventBridge invokes a Lambda function (Region A)
- The Lambda function executes the Fargate task (Region A)
- The Fargate task reads the changes from the Region A CodeCommit repository and copies them to the Region B CodeCommit repository.
# EventBridge event
{
"detail-type": "CodeCommit Repository State Change",
"source": "aws.codecommit",
"account": "123456789012",
"region": "us-east-1",
"resources": ["arn:aws:codecommit:us-east-1:123456789012:myRepo"],
"detail": {
"event": [
"referenceCreated",
"referenceUpdated"
],
"repositoryName": "myRepo",
"repositoryId": "12345678-1234-5678-abcd-12345678abcd",
...
}
}

