Systems Manager (formerly known as SSM) manages EC2 instances at scale (EC2 fleet).
Features
- Systems Manager organizes and groups your EC2 instances.
- Automates common tasks such as patching, running scripts, and installing applications.
- An SSM agent needs to be installed on each VM.
- An agent is installed by default in some AMIs such as Amazon Linux 2.
- Resource Groups
- A Resource Group is a logical grouping of resources in a single region using tags.
Parameter Store

Parameter Store provides secure serverless storage for the management of configuration data and secrets.
Features
- You can store confidential data such as passwords, database strings, and license codes as parameter values.
- Values can be saved as plain text or encrypted values (using the key from KMS).
- Parameters are stored in hierarchies.
- e.g. /prod/db/aurora/connection, /dev/db/aurora/connection
- The service can be used with EC2, ECS, or Lambda.
Tiers
| Standard | Advanced |
|---|---|
| up to 10,000 parameters | more than 10,000 parameters |
| up to 4KB parameter value size | up to 8KB parameter value size |
| No parameter policies | parameter polices are available |
| No charge | Charges apply |
Types
- String
- Any string value
- StringList
- a comma-separated list of strings
- SecureString
- Encrypted string using the KMS key from your account or another account
Parameter Policies
- You can assign a TTL (Time To Live – Expiration) to a parameter.
- Or Send a notification to EventBridge as an event
- x days before expiration
- for x days, a parameter has not been updated
# delete a parameter
{
"Type": "Expiration"
"Attributes": {
"TimeStamp": "2025-12-31T12:00:00.000Z"
}
}
# notify before 15 days the parameter expires
{
"Type": "ExpirationNotification"
"Attributes": {
"Before": "15",
"Unit": "Days"
}
}
# notify when there is no update for 30 days
{
"Type": "NoChangeNotification"
"Attributes": {
"After": "30",
"Unit": "Days"
}
}
Patch Manager

- Automates the process of patching managed instances
- Supports:
- EC2 instances and on-premise instances
- Linux, Windows, and MacOS
- Patches can be done on-demand or on a schedule using Maintenance Windows
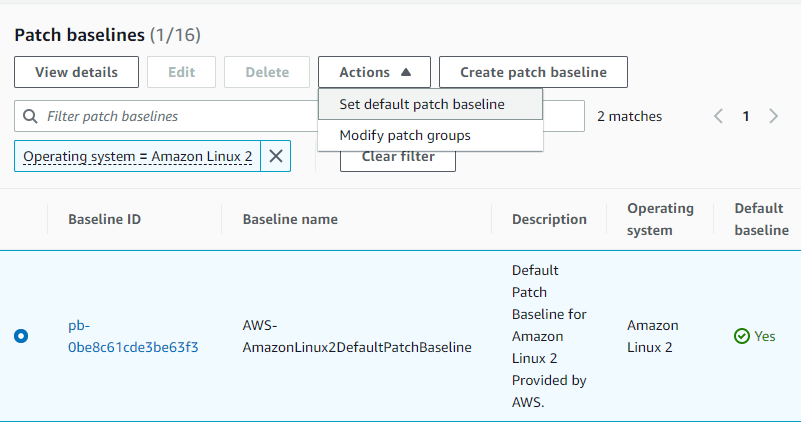
- “Patch Baseline” defines which patches will be installed
- Pre-defined
- Managed by AWS for different OSs
- Cannot be modified
- Managed by AWS for different OSs
- Custom
- You can create your own Patch Baseline.
- Pre-defined
- Run Patch Baseline
- You can use “Run Command” with AWS-RunPatchBaseline (SSM Document)
- Run both OS & application patches
- You can use “Run Command” with AWS-RunPatchBaseline (SSM Document)
- Patch Group
- A set of instances with a specific Patch Baseline
- Instances should be defined with a tag key “Patch Group“
- An instance should belong to only one Patch Group.
- A Patch Group can be associated with only one Patch Baseline.
Tutorial
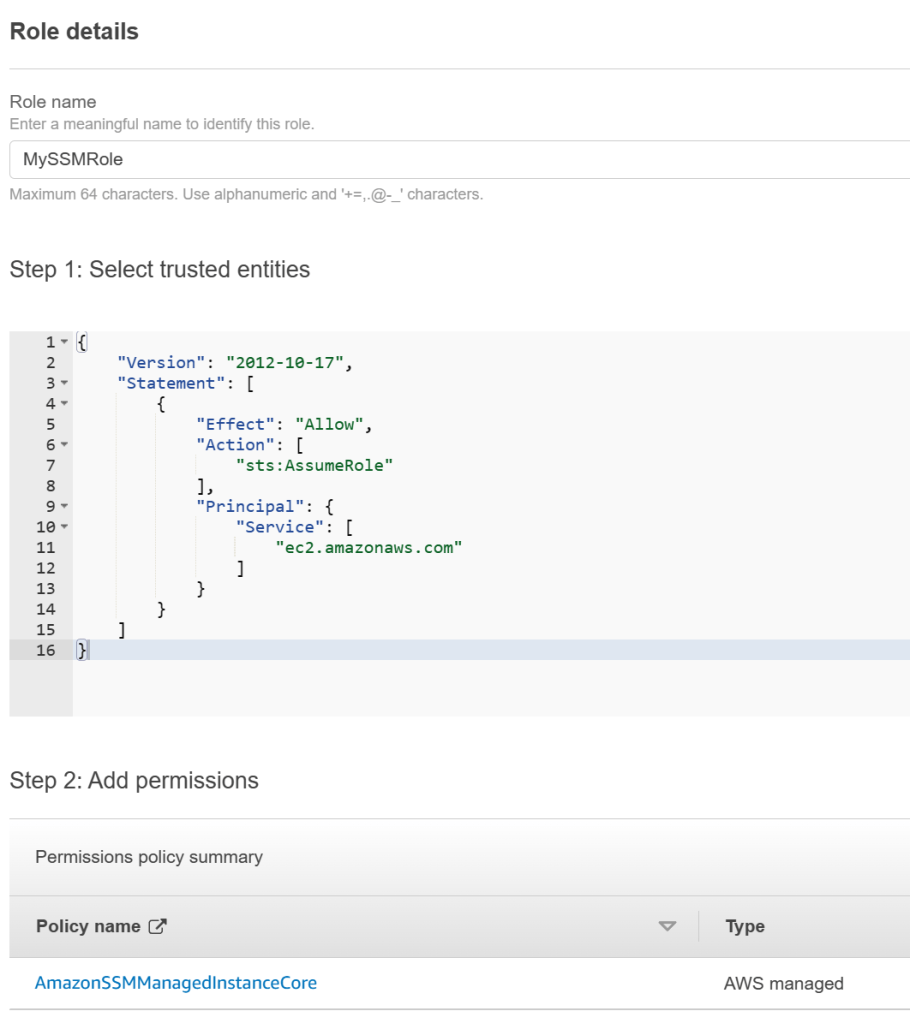
- Create an IAM role
- Trusted Entity: EC2
- Managed Policy: AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
- Launch EC2 instances – 2 or more
- Attach the role
- Provide a tag to group instances later
- Open the Systems Manager Console
- You can find instances in the Fleet Manager section.
- If you do not see the instances, please check the attached IAM role in the EC2 instances.
- Create a resource group
- Search and select the service “Resource Groups & Tag Editor“
- Create a resource group based on a tag
- Use Patch Manager in the Systems Manager
- Search the baseline and set it as the default
- Use Patch Manager – Patch Now
- You can schedule the patch or patch now.
- You can select target instances using instance tags or a resource group.
- Install any missing patches
Maintenance Windows

- Maintenance Windows define a schedule of when to perform actions on selected instances, such as patching.
- You need to define:
- Schedule
- Duration
- A set of instances
- A set of tasks
Run Command

“Run Commands” allows you to run operational tasks across multiple EC2 instances.
- Run commands or scripts on one or more EC2 instances using Resource groups.
- Type the command directly or select/create the SSM Document
- No need to use SSH
- Use Cases
- Stop, start, re-size, or terminate instances.
- Install, patch, or uninstall software.
- Integration
- Can be invoked via EventBridge
- Outputs can be sent to S3 or CloudWatch Logs.
- A notification can be sent to SNS.
Example: Run Command
- Setup an IAM role with AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
- Launch EC2 instances – 2 or more
- Create a resource group and add the instances to the group
- Run Command
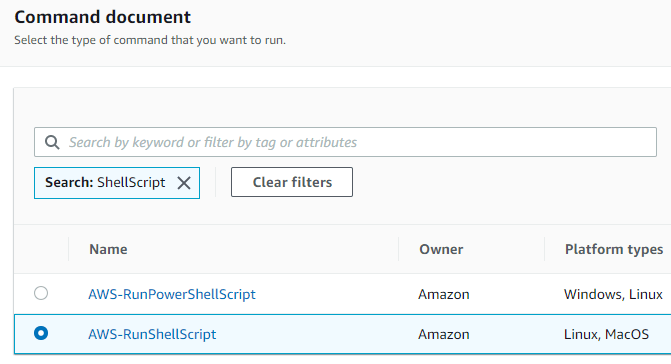
- Select the Command document
- For your custom action, you can select “AWS-RunShellScript“
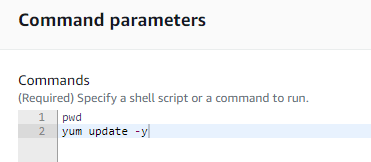
- Type the commands in the Command parameters
- Select your target using the resource group
- You can save the output in S3 or set up the SNS notification.
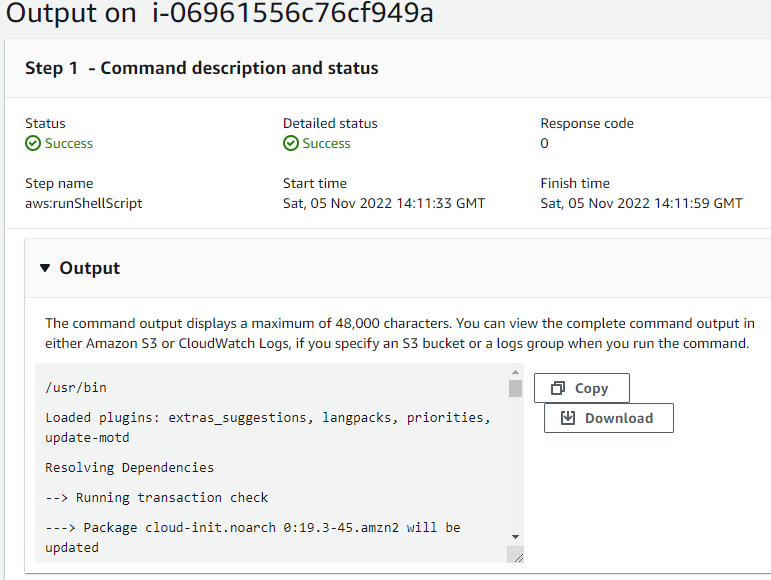
- Run the command
- You can confirm the output in Management Console.
Automation

- SSM Automation simplifies common maintenance tasks automatically.
- EC2 Instances, AMIs, EBS Snapshots, RDS Instances …
- Automation Runbook
- SSM Document of type “Automation”
- Triggers
- Manually using Console, CLI, or SDK
- EventBridge (events or schedule)
- Maintenance Windows (schedule)
- AWS Config remediations
(1) Managing EC2 instances and RDS DB Instances
- Start Instances
- AWS-StartEC2Instance
- AWS-StartRdsInstance
- Stop Instances
- AWS-StopEC2Instance
- AWS-StopRdsInstance
- Resize Instances – (reduce costs by downsizing underlying instances)
- AWS-ResizeInstance
(2) Automatically build AMIs that can be shared across applications
- SSM Automation is triggered.
- Automation creates an image
- AWS-CreateImage
- Automation triggers an event (AMI available) to EventBridge (ami-id as a parameter)
- EventBridge invokes Lambda function to do the post job
- Stores an AMI id in the Parameter Store so that the id can be shared
(3) Automatically remediate non-compliant configurations using AWS Config
For example, you set up the rule that all S3 buckets must enable versioning.
- Detect the bucket, whose versioning is not enabled
- “AWS Config” detects the non-compliant configuration
- “AWS Config” automatically remediate the issue
- Run SSM Automation “AWS-ConfigureS3BucketVersioning“
Documents

In Documents, you can define actions and run commands in them.
- JSON or YAML
- Versioning is supported.
- You can define:
- Parameters
- Actions
- Commands
- Can be used in:
- SSM Run Command
- SSM Patch Manager
- SSM Automation (with AWS Config)
---
schemaVersion: '2.2'
description: State Manager Bootstrap Example
parameters: {}
mainSteps:
- action: aws:runShellScript
name: configureServer
inputs:
runCommand:
- sudo yum install -y httpd24
- sudo yum --enablerepo=epel install -y clamav
---
schemaVersion: "2.2"
description: "Example document"
parameters:
Message:
type: "String"
description: "Example parameter"
default: "Hello World"
mainSteps:
- action: "aws:runPowerShellScript"
name: "example"
inputs:
timeoutSeconds: '60'
runCommand:
- "Write-Output {{Message}}"
Session Manager
- allows to start a secure shell to EC2 instances
- No need of SSH setup, bastion hosts, or Key pairs
- Access through AWS console, AWS CLI, or Session Manager SDK
- supports Linux, Windows, & MacOS
- Monitoring
- Logs can be sent to S3 or CloudWatch Logs
- Security
- Use IAM to restrict which user can use Session Manager
Using SSM Session Manager in Private Network only
- Install the SSM agent in EC2 instances
- Attach an IAM policy providing the required SSM permissions to an existing IAM instance profile
- AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
- Use tags to restrict access to only specific instances
- Create a VPC interface endpoints for Systems Manager in the relevant AWS Region to provide private access
- .ssm: a VPC endpoint for the SSM service
- .ssmmessages: a VPC endpoint for the SSM Session Manager
- Allow 443 inbound traffic in the security group of both endpoints
- Allow 443 outbound traffic in the security group of EC2 instances
- (Optional) Create VPC endpoints for your scenario
- A VPC interface endpoint for KMS
- A VPC interface endpoint for CloudWatch Logs
- A VPC gateway endpoint for S3 bucket (logs)
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ssm:StartSession",
"Resource": "arn:aws:ec2:<region>:<account>:Instance/*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"ssm:resourceTag/Environment": ["dev"]
}
}
}

Hybrid Activation
You can use Systems Manager to manage on-premise servers.
- You need to register on-premise instances with an Activation Code.
- SSM-managed servers use the prefix –
- EC2 instances: “i-“
- Hybrid managed instances: “mi-“
Hybrid Activation Process
- In Systems Manager, create “Hybrid Activation”
- Systems Manger returns
- Activation Code and Activation ID
- Install an SSM agent in the on-premise instances
- Register on-premise instances using the Activation Code and the Activation ID
- Or you can setup API Gateway and Lambda function to register instances.
- Once instances are registered, you can use System Manager functionalities on these instances:
- You can use “Systems Manager Maintenance Window” to schedule the actions such as patching